Dog obesity refers to the increase and excess fat tissue in the dog's body. Generally speaking, a dog's weight exceeds 15% of its normal value is obesity. In developed countries and regions, 24%-44% of dogs are overweight, while underweight...
Dog obesity refers to the increase and excess fat tissue in the dog's body. Generally speaking, a dog's weight exceeds 15% of its normal value is obesity. In developed countries and regions, 24%-44% of dogs are overweight, while underweight lean dogs account for only 2%-3%.
Obs in dogs are basically due to the body's total energy intake exceeds consumption, and the remaining part accumulates in the form of fat. Most dogs are obesity due to overeating. This is the most common nutritional disease in dogs with good living conditions, and its incidence is much higher than that of various nutritional deficiency.

1. Causes of dog obesity:
The main causes of dog obesity The intake of foot energy exceeds consumption. There are many factors that cause dog obesity: 1. Overnutrition. Improvement of food palatability and popularization of free feeding methods have resulted in excessive feeding and insufficient exercise, which are the main reasons for overnutrition. 2. Related to age, gender and breed. As we get older, obesity becomes more likely, and females are more likely to occur than males; beagles, cocker spaniels, German shepherds, Yorkshire, Dachshunds, Labradors, etc. are all breeds that are prone to obesity. 3. Endocrine dysfunction. Such as sterilization surgery, pituitary tumors, hyperadrenal function, excess insulin secretion, hypothalamic hypofunction, hypothyroidism, etc., may lead to obesity. 4. Other diseases. For example: Dogs suffering from respiratory diseases, kidney diseases, and heart diseases are also prone to obesity.
5. Genetic factors, such as obese dogs, their offspring are also prone to obesity.
2. Key points for diagnosis of dog obesity: 1. The body is round and plump, with rich subcutaneous fat, weakened physical strength, easy fatigue, and unbearable heat. 2. Mild obesity sometimes leads to indigestion, decreased libido and dermatitis. 3. Highly obese because of fat heart, there is difficulty breathing, hyperactivity of heart throbbing, and increased pulse. 4. Canines suffering from obesity have elevated blood cholesterol and blood lipids. Due to blood circulation disorders, liver, kidney or pancreatic dysfunction may be secondary.
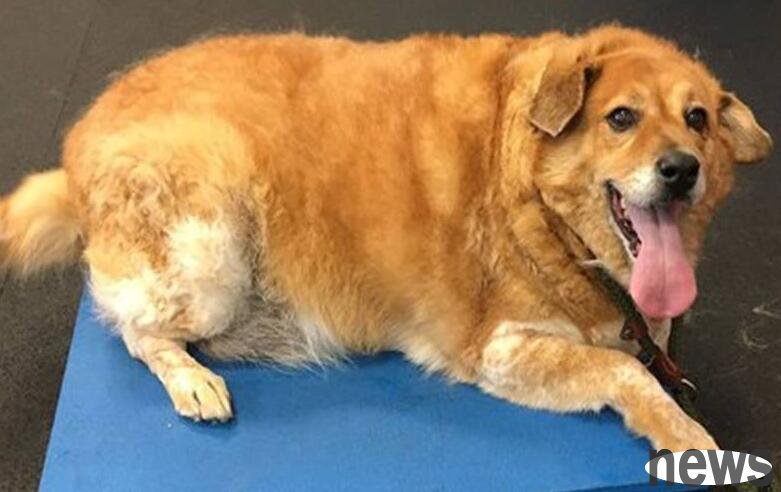
III. Preventive measures for dog obesity:
The prevention and treatment of dog obesity should focus on prevention. The following measures can be taken in the treatment: 1. Dietary therapy is reduced: formulate a plan to limit food supply and obtain full understanding and full cooperation from all relevant personnel. To reduce the amount of food and the number of times you give your dog, you can feed only 60%-70% of the usual amount every day, and feed it regularly and regularly and regularly and quantitatively in 3 or 4 times. Feed prescription foods for weight loss with high fiber, low energy, and full nutritional price. It is better to reduce weight by 1% to 2% per week. Once the weight reaches the standard weight, determine and provide the necessary maintenance food. 2. Exercise therapy: Let the dog perform regular and moderate-intensity exercise for 20 to 30 minutes every day. 3. Treat the primary disease that causes obesity. 4. Drug weight loss: You can eat appetite inhibitors such as cholecystectomy, emetic agents, amylase blockers, etc.; use thyroid cords, growth hormones, etc. to improve metabolic efficiency. 5. Preventing animal obesity during the developmental period is the most effective way to prevent obesity in adult animals. In addition, we should prevent weight gain again after successful weight loss.